
Welcome to my blog, “The Social Determinants of Health: Addressing Inequalities”. This blog will explore the social determinants of health, their impact on health inequalities, and strategies to address them. We will look at the causes of health inequalities and the programs in place to help reduce them. Your knowledge of the social determinants of health and the strategies for addressing them to minimize health inequalities will have increased by the time you conclude this blog. Let’s dive in right now!
What are the Social Determinants of Health?
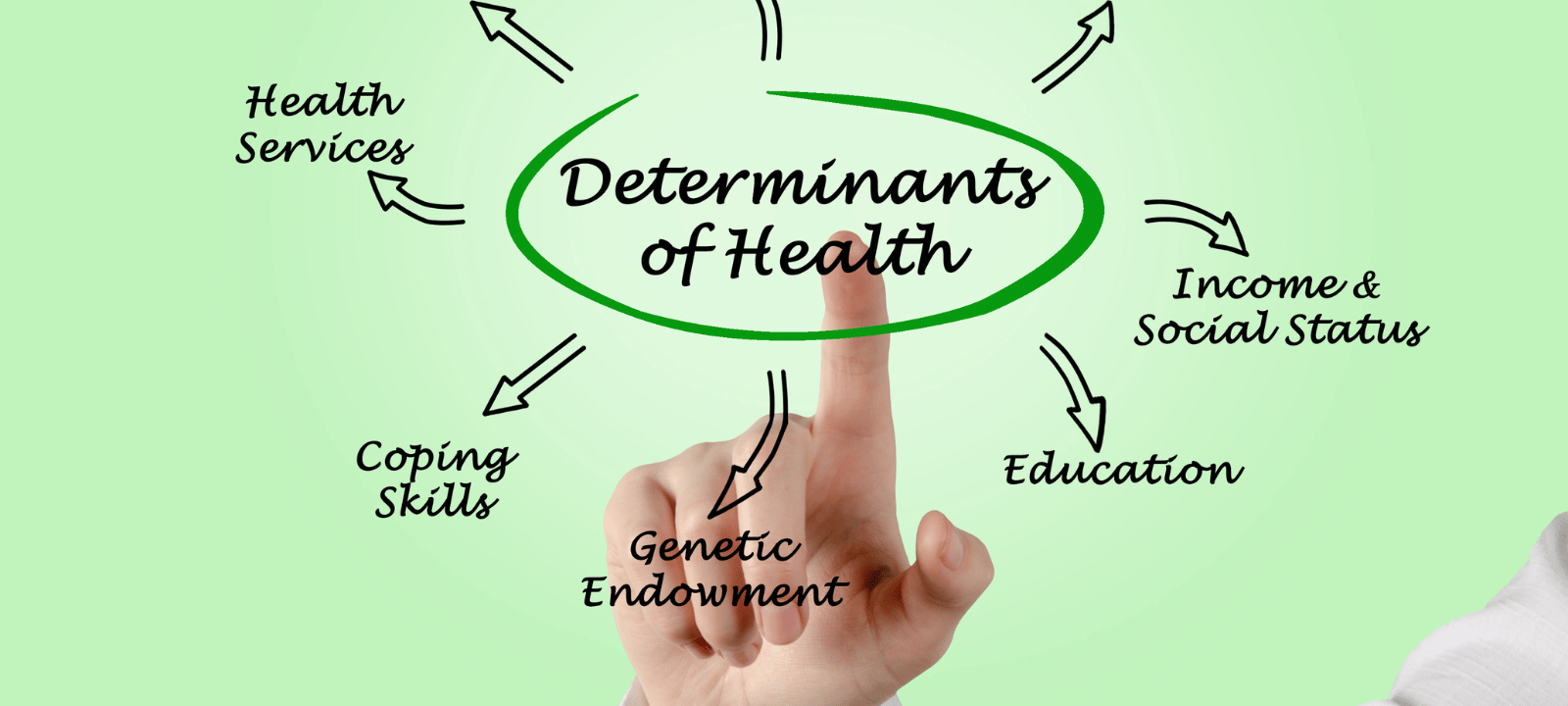
The circumstances of a person’s birth, upbringing, residence, employment, and old age are all social determinants of health (SDOH). The global, national, and local distribution of money, power, and resources shapes these conditions. Health inequalities, the unjust and preventable variations in health status found within and across nations, are primarily attributable to the socioeconomic determinants of health.
Examples of Social Determinants of Health:
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies five critical social determinants of health:
- Education: People with greater levels of education are more likely to take better care of their health, have better access to healthcare, and know more about potential health hazards.
- Income and social status: Income and social status are closely linked to health outcomes. Health concerns, such as poverty and homelessness, are less probable for those with more excellent wages and social standing since they are more likely to access better healthcare, nutrition, and shelter.
- Employment: Employment status can significantly impact health outcomes. Those who are unemployed are more likely to experience poverty and be unable to access healthcare.
- Social support networks: Social support networks are essential for health outcomes. Those with strong social networks are more likely to have better mental health and access to resources and support.
- Access to healthcare: Access to healthcare is critical in determining health outcomes. Those who can afford medical care are more likely to have regular checkups and seek treatment when sick.
How Social Determinants Impact Health:
Health outcomes are affected immediately and over time by the socioeconomic determinants of health. They can affect health directly by influencing access to healthcare and health-related resources and indirectly by influencing factors such as education, employment, and social support networks.
For example, those with higher levels of education are more likely to have access to better healthcare, be more informed about health risks, and take better care of their health. Similarly, those with higher incomes and social status are more likely to have access to better healthcare, nutrition, and housing and are less likely to experience health risks such as poverty and homelessness.
The social determinants of health also play an essential role in health inequalities. Disparities in health status that exist both within and across nations are called health disparities. The social determinants of health primarily cause these inequalities and can lead to worse health outcomes for those with lower incomes, lower levels of education, and less access to healthcare.
Understanding the social determinants of health and how they impact health outcomes makes it possible to develop strategies to address health inequalities and improve health outcomes for all.
Health Disparities and Their Social Roots

The social determinants of health (SDH) are the underlying factors that affect health and well-being. These factors include economic stability, education, employment, housing, social support, and access to health care. These things can negatively affect our health and create health disparities.
How Social Determinants Impact Health Inequalities:
Social factors have a significant effect on health disparities. Poor people are likelier to suffer from poor health, as they often lack access to necessities such as nutritious food, safe housing, and quality health care. Additionally, poor people may need more access to education, employment, and social support, which can help their health.
Examples of Health Inequalities:
There are several manifestations of health disparity. The impoverished have a higher prevalence of chronic illnesses, including diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Furthermore, health inequities such as more excellent newborn mortality rates and poorer life expectancy are more prevalent among persons of color.
The Role of Social Determinants in Health Inequalities:
The role of social determinants in health inequalities is significant. Social determinants can directly impact health, as those living in poverty are more likely to suffer from poor health due to limited access to basic necessities. Additionally, social determinants can indirectly impact health, as those living in poverty are more likely to suffer from poor mental health due to poverty-related stressors.
Understanding socioeconomic factors’ impact on health is crucial for addressing health inequities. We can help eliminate health inequalities and provide everyone a fair shot at a long, healthy life by focusing on the underlying socioeconomic determinants of health.
Recognizing the Roots of Health Disparities
The term “health inequalities” describes discrepancies in health status between groups of people. These differences can be based on race, gender, socioeconomic status, and geography. While many factors contribute to health inequalities, one overarching cause is social determinants of health.
What Causes Health Inequalities?
When resources and chances for accessing healthcare and other services are distributed unequally, it results in health inequities. These disparities can be seen in unequal access to quality healthcare, education, housing, and employment opportunities. As a consequence of these disparities, those with less access to healthcare and other resources are more likely to have poor health outcomes.
How Social Determinants Contribute to Health Inequalities
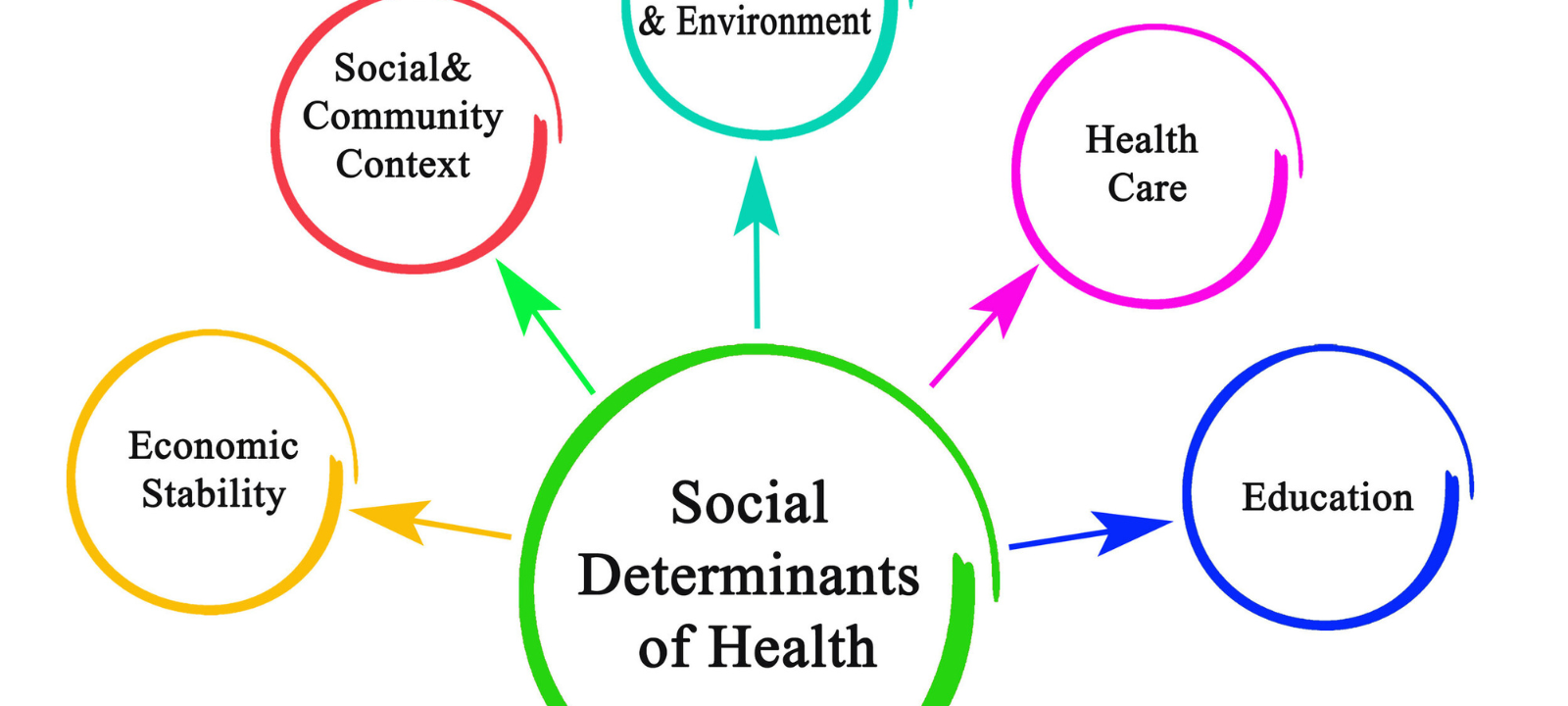
The circumstances of a person’s birth, childhood, adulthood, and old age are all social determinants of health. The global, national, and local distribution of money, power, and resources shapes these conditions. Social determinants of health can include income, education, occupation, housing, and access to healthcare. These factors can significantly impact health outcomes, as those with fewer resources and opportunities are more likely to experience poorer health outcomes.
The Role of Socioeconomic Factors in Health Inequalities
Health disparities may be traced back to social and economic issues. These factors include income, education, occupation, and access to healthcare. Low income and education levels are linked to poorer health outcomes, as those with fewer resources and opportunities are more likely to experience poorer health outcomes. Furthermore, those with lower means are more likely to have restricted access to medical treatment, which may result in less favorable health outcomes.
Socioeconomic factors can also lead to disparities in access to quality healthcare. Health outcomes may be worse for those with lower earnings since they are more likely to have restricted access to healthcare. In addition, those with lower levels of education are more likely to have limited access to healthcare, which can lead to poorer health outcomes.
By understanding the causes of health inequalities, we can develop strategies to address them. The socioeconomic determinants of health may be addressed to improve everyone’s social justice and equity.
Strategies to Address Health Inequalities

Reducing the gaps in health outcomes between various social groups aims to address health inequalities. Health policymakers and communities must work together to identify and implement strategies to reduce health inequalities.
Strategies to Reduce Health Inequalities:
Several strategies can be used to reduce health inequalities. These include:
- Improving access to quality healthcare services: Health inequalities can be reduced by providing access to quality healthcare services. This includes providing access to preventive care, such as immunizations, screenings, health education, and treatment for chronic conditions.
- Increasing access to healthy food options: Health inequalities can be reduced by providing access to healthy food options, such as fruits and vegetables. This can be done by providing access to affordable, healthy food options in low-income areas and through education about the importance of healthy eating.
- Reducing exposure to environmental hazards: Health inequalities can be reduced by reducing exposure to environmental hazards, such as air pollution and water contamination. This can be done by increasing access to clean air and water and enforcing regulations that limit exposure to environmental hazards.
- Promoting healthy behaviors: Health disparities may be decreased by encouraging healthy habits like exercise and abstaining from cigarettes. This can be done by providing access to recreational facilities and education about the importance of healthy behaviors.
The Function of Policy in Reducing Health Disparities

To effectively address health inequalities, policymakers must create and implement policies that target the root causes of health disparities. These policies should focus on improving access to quality healthcare services, increasing access to healthy food options, reducing exposure to environmental hazards, and promoting healthy behaviors.
The Role of Communities in Addressing Health Inequalities:
In addition to policymakers, communities also play an essential role in addressing health inequalities. Communities may collaborate to uncover the underlying causes of health disparities, take action against them, and develop and implement measures to lessen them. This includes providing access to quality healthcare services, increasing access to healthy food options, reducing exposure to environmental hazards, and promoting healthy behaviors.
By working together, policymakers and communities can create and implement strategies to reduce health inequalities and improve health outcomes.
Examples of Programs Aimed at Addressing Inequalities
Health inequalities are a significant challenge faced by many countries around the world. To address these inequalities, governments, organizations, and individuals are increasingly implementing programs to reduce disparities in health outcomes. Examples of such programs include:
- Community Health Workers: To underprivileged groups, community health professionals provide services in illness prevention, health promotion, and health education. These employees often have a thorough awareness of the neighborhood and the unique requirements of its inhabitants, enabling them to customize their services to the demands of the clientele.
- Health Insurance Programs: Health insurance plans are created to provide those who would not otherwise be able to afford them access to medical treatment. The government often subsidizes these programs and can help to reduce disparities in health outcomes by making health care more accessible and affordable.
- Access to Healthy Foods: Programs to increase access to healthy foods are becoming increasingly popular. These programs provide access to fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to those who may not otherwise be able to afford them. This can help reduce disparities in health outcomes by ensuring all individuals have access to nutritious foods.
- Health Education Programs: Health education programs are designed to increase awareness about health issues and promote healthy behaviors. Promoting healthy behaviors and enhancing awareness and understanding of health-related problems will aid in the reduction of inequalities in health outcomes.
The Impact of Programs Aimed at Addressing Health Inequalities:
The impact of programs aimed at addressing health inequalities can be significant. Expanding access to health care services, making healthy foods available, and encouraging healthy behaviors will aid in reducing inequities in health outcomes. Additionally, these programs can help reduce the disease burden on individuals, families, and communities, leading to improved health outcomes and quality of life.
How to Find Programs Aimed at Addressing Health Inequalities:
There are various ways to find programs to address health inequalities. Many government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community-based organizations offer programs to reduce disparities in health outcomes. Additionally, individuals can search online for programs that address health inequalities. Finally, individuals can contact their local health department or healthcare provider to inquire about available programs.
Conclusion
The social determinants of health are complex and varied, but they are also powerful drivers of health inequalities. We may start to create solutions to alleviate health inequities by recognizing their underlying causes. Programs like the Affordable Treatment Act, Medicaid expansion, and Community Health Centres have effectively given those without access to treatment and services. However, it is also essential to focus on the social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and access to resources. By tackling these problems, we may contribute to improving everyone’s health and reducing health inequalities.
Recognizing the significance of socioeconomic determinants of health in tackling health inequities is crucial as we proceed. By understanding the underlying causes of health disparities, we can develop effective strategies and programs to ensure everyone can access the healthcare and resources they need. Together, we can work to ensure that all individuals have the opportunity to live healthier, more equitable lives.



