Are you curious about why anesthesia makes you sleep? Have you ever wondered what it is and how it works? In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of anesthesia and how it affects the body. We’ll look at the different types of anesthesia and their effects and potential side effects. Finally, we’ll discuss how anesthesia makes you sleep. So, if you’re curious about anesthesia and its effects on the body, read on!
What is Anesthesia?
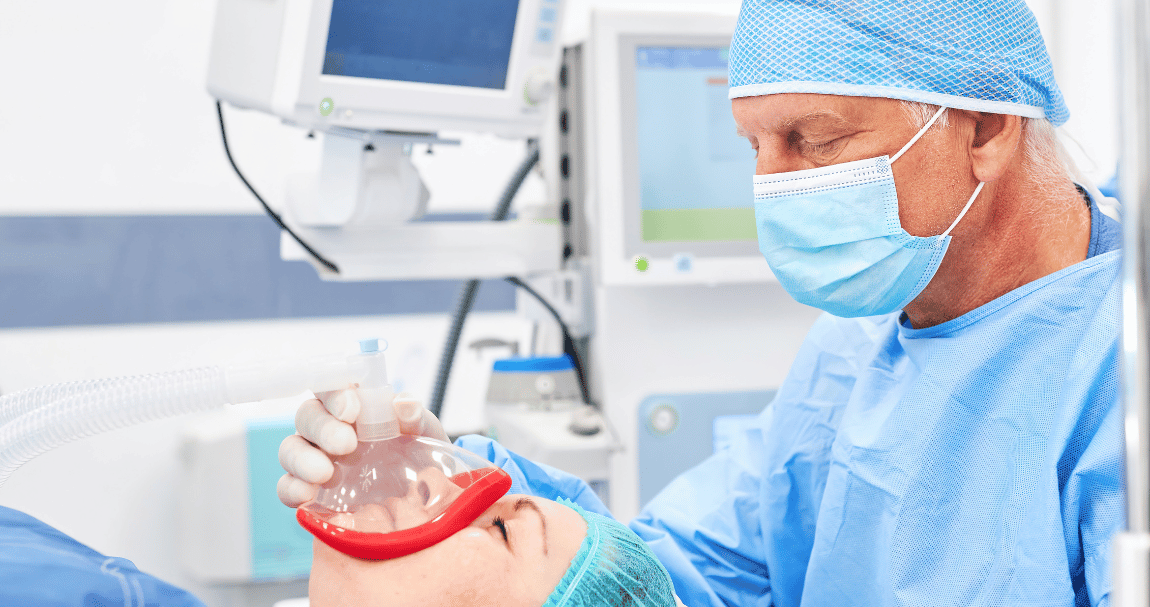
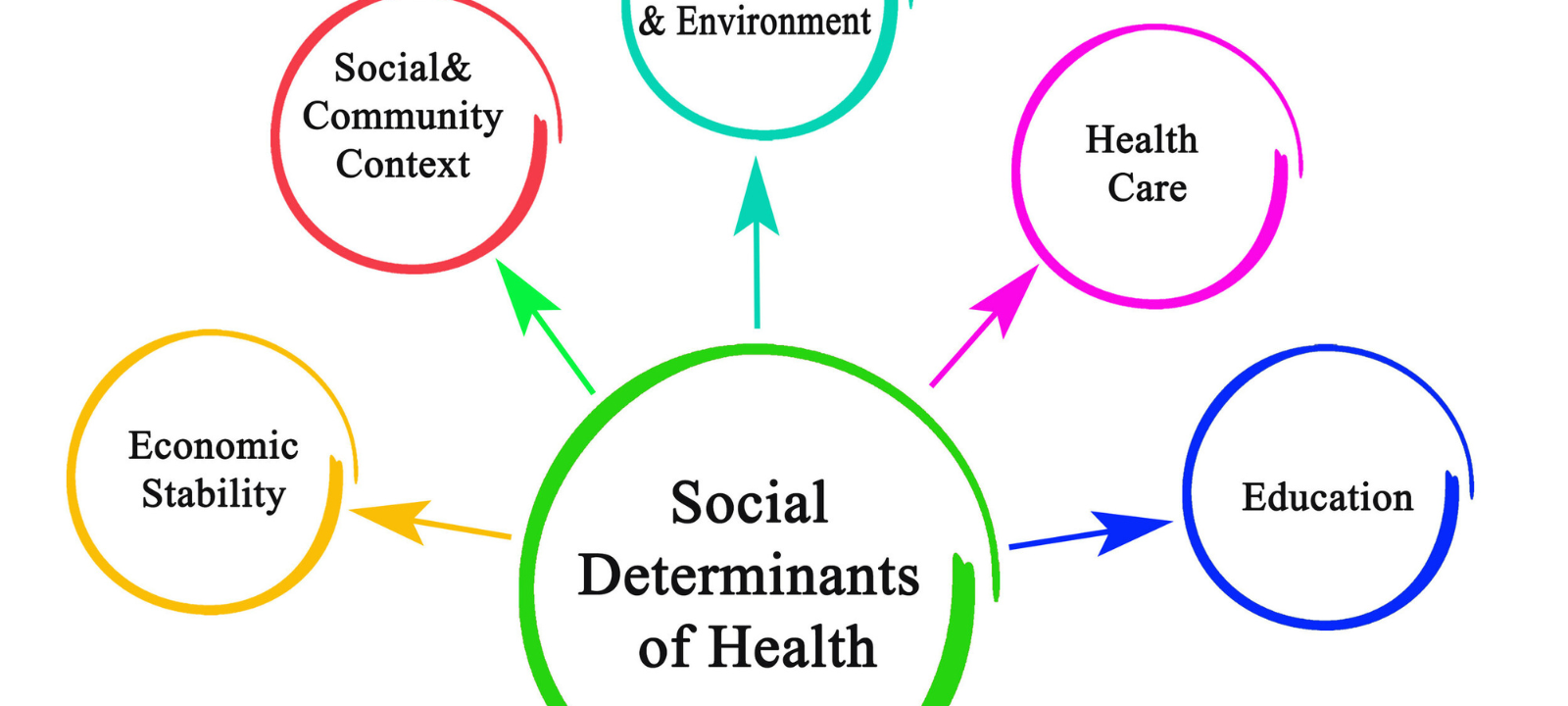
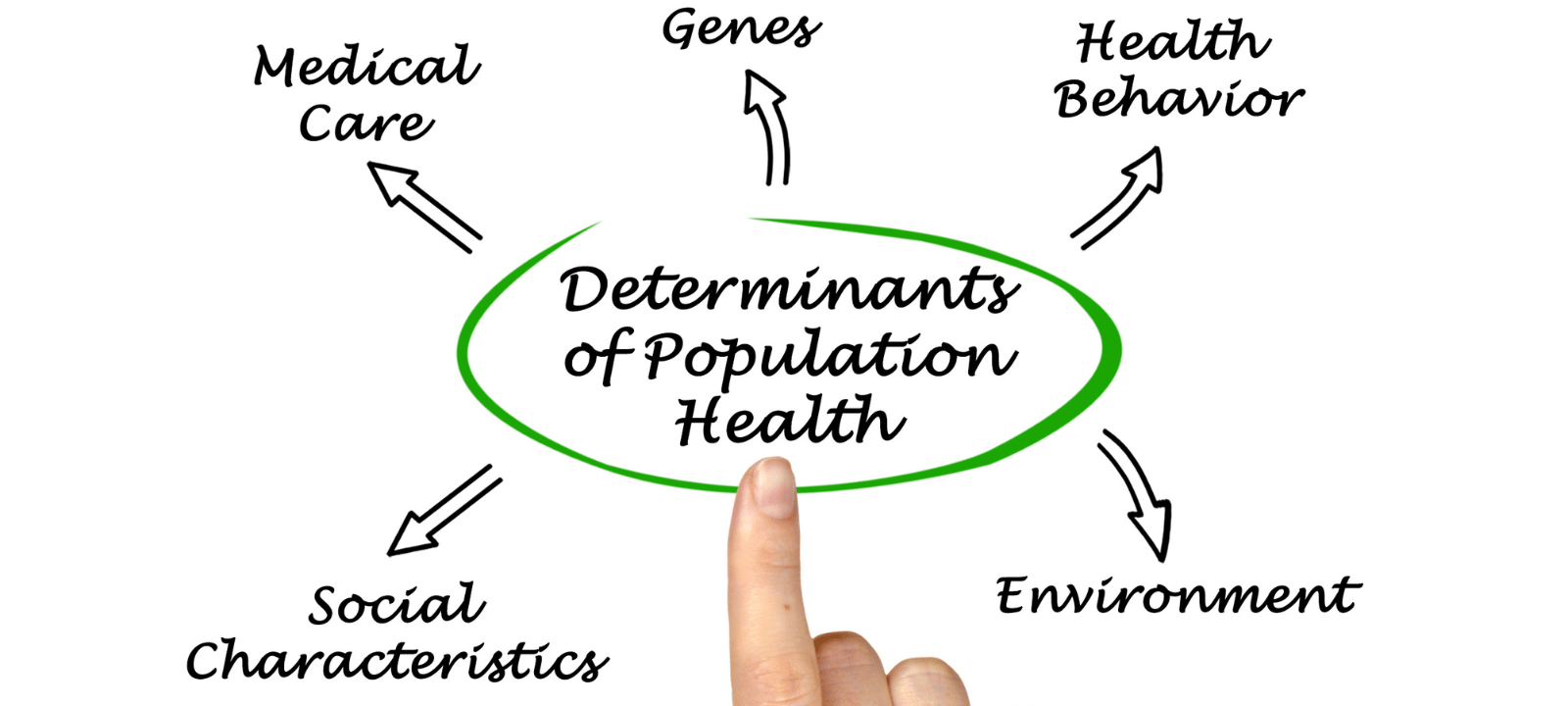
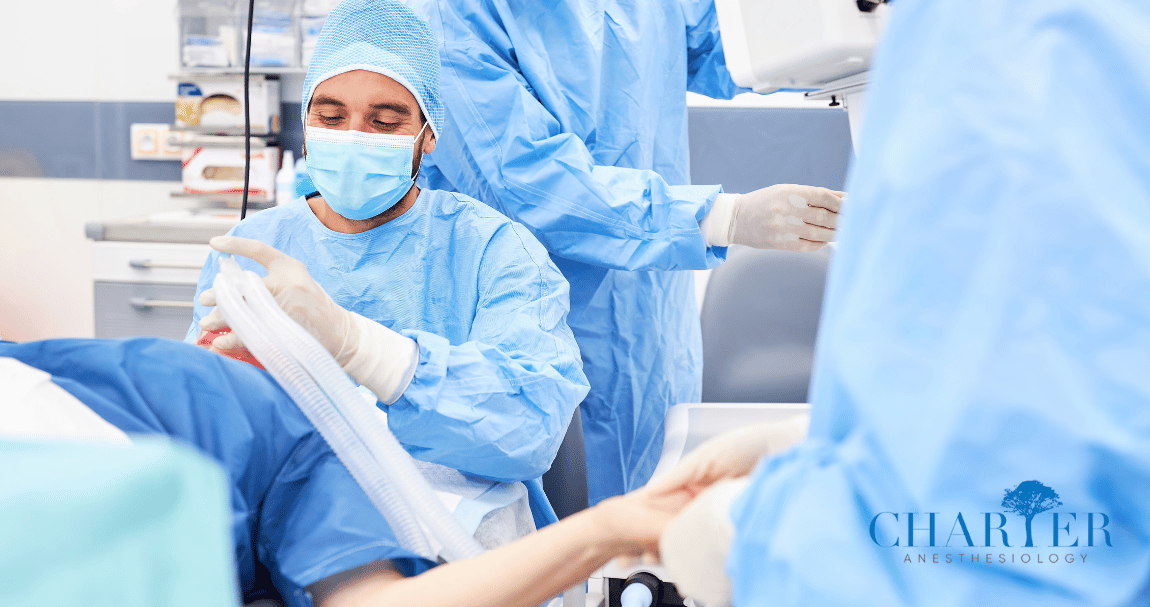
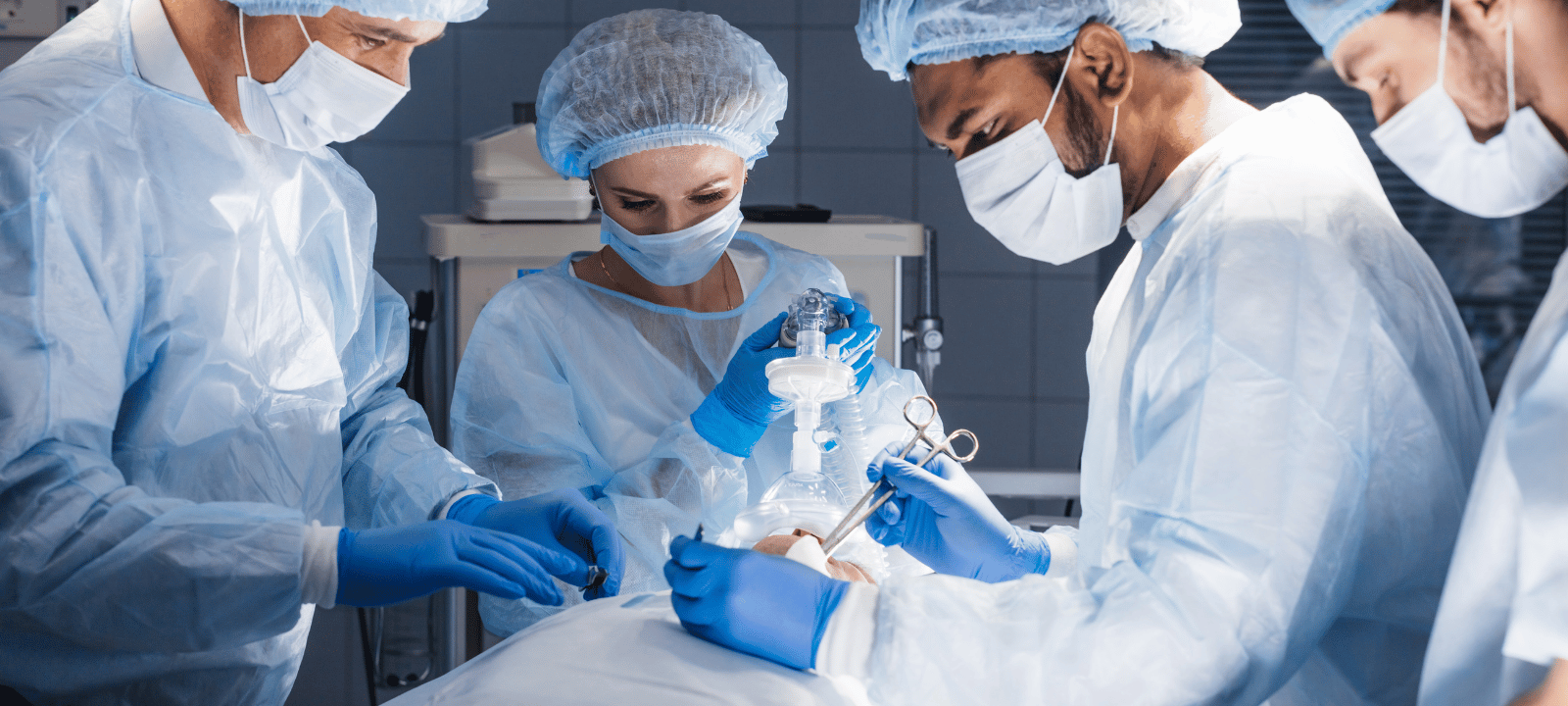
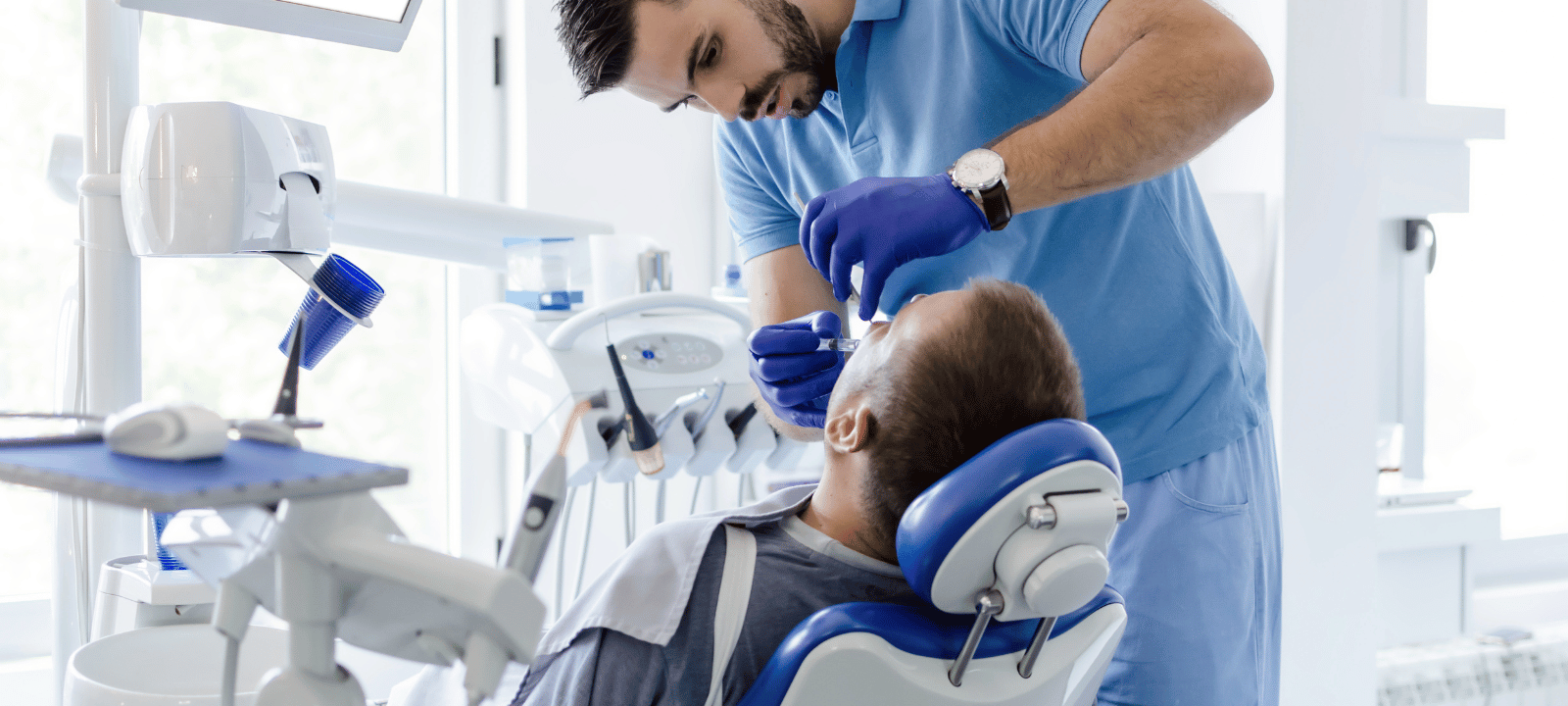
Anesthesia is a medical practice that uses drugs to block pain. It makes a patient unconscious or insensible to pain during a medical procedure. Anesthesia is used to help patients undergo various medical procedures, including surgery, endoscopies, dental work, and childbirth. Anesthesia is administered by an anesthesiologist, a medical professional specializing in administering and monitoring the effects of anesthesia.
Provide a Definition of Anesthesia:
To temporarily numb the pain feeling, anesthesia is a medical practice. It makes a patient unconscious or insensible to pain during a medical procedure. Anesthesia is administered by an anesthesiologist, a medical professional specializing in administering and monitoring the effects of anesthesia.
Explain the Purpose of Anesthesia:
The purpose of anesthesia is to make a patient unconscious or insensible to pain during a medical procedure. Anesthesia helps to reduce the stress and discomfort associated with medical procedures, allowing them to be completed safely and effectively. The danger of problems during surgery and other medical procedures is also lowered with the use of anesthesia.
Discuss the Different Types of Anesthesia:
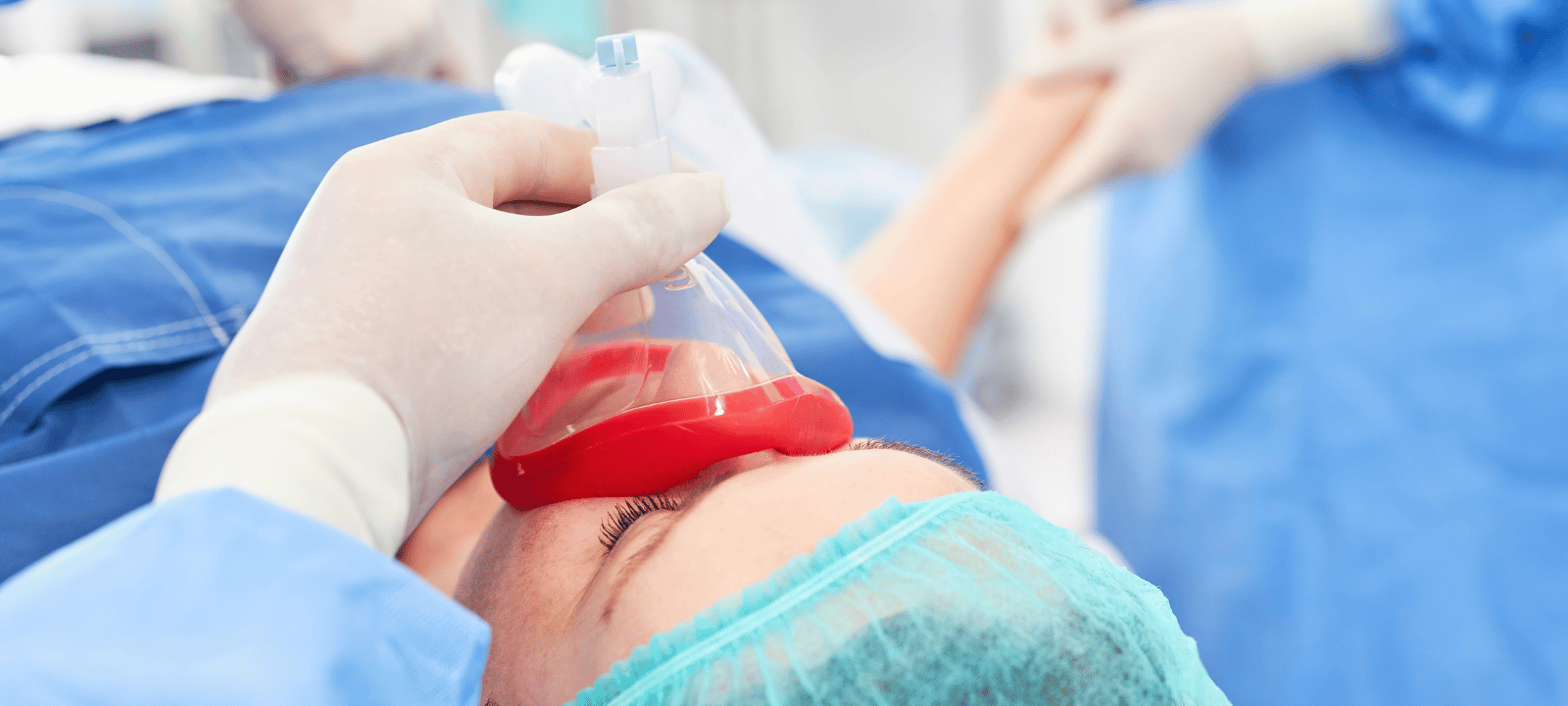
General, regional, and local anesthesia are the three basic categories. A patient is rendered unconscious during surgery using general anesthesia. During delivery, regional anesthesia is used to numb a particular body part, such as the bottom half of the body. Local anesthesia is used to numb a small body area, such as the area around a wound. Each type of anesthesia has different effects and risks associated with it.
Anesthesia is a powerful tool to make medical procedures safer and more comfortable for patients. Understanding the different types of anesthesia and their effects is essential to choosing the best option for each patient.
How Does Anesthesia Work?
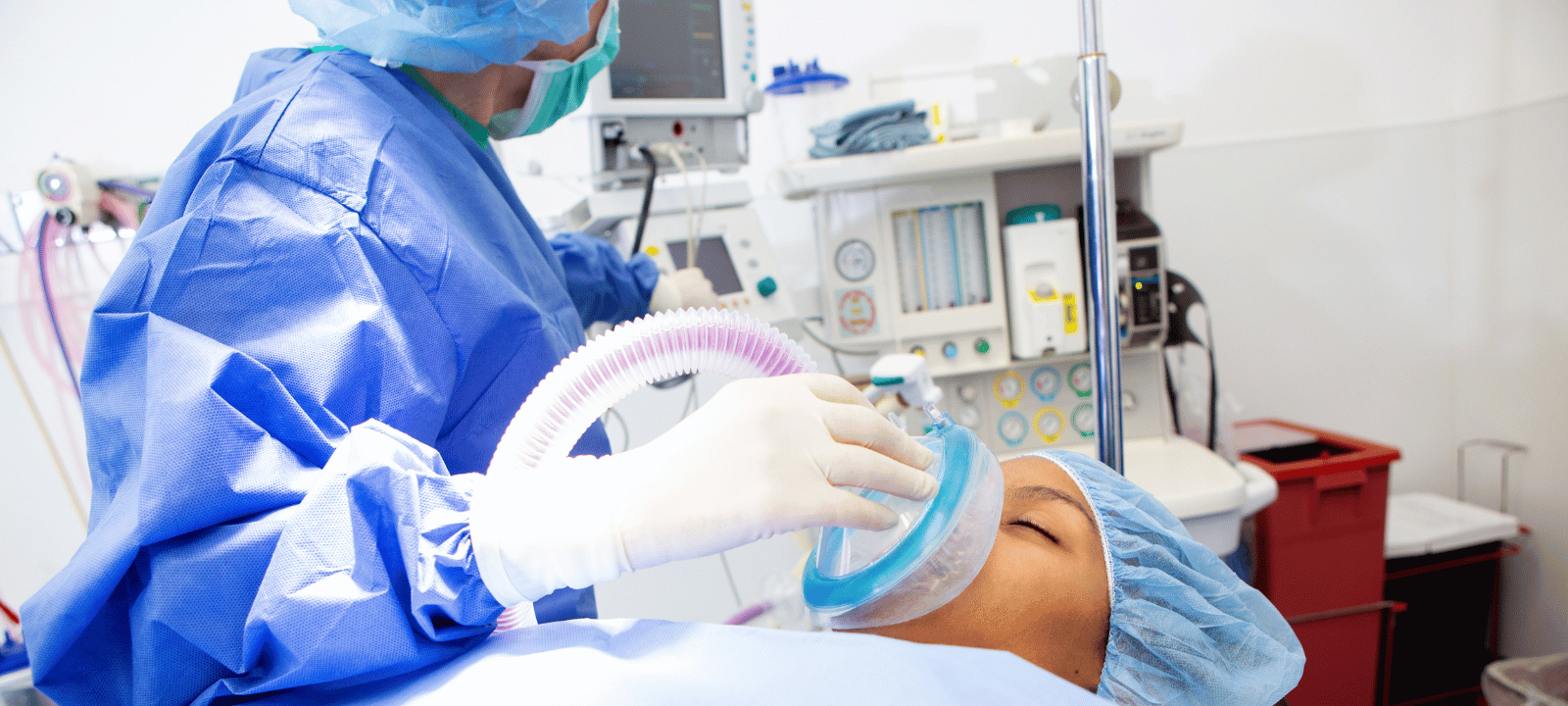
During anesthesia, a medical technique, drugs block the body’s pain receptors. It can be administered in various ways, including intravenously, orally, and through inhalation. Anesthesia works by blocking the transmission of pain signals from the body to the brain. It also affects the nervous system by slowing down the production of neurotransmitters responsible for sending pain signals.
When anesthesia is provided, it reduces the neurological system’s activity, lessening the body’s capacity to feel pain. This is why anesthesia is used during surgery and other medical procedures. It helps to reduce the amount of pain experienced by the patient.
Anesthesia works by blocking the transmission of pain signals from the body to the brain. It does this by blocking the release of neurotransmitters, which transmit pain signals from the body to the brain. Anesthesia also affects the nervous system by slowing the production of neurotransmitters that send pain signals.
Anesthesia also works by blocking the receptors in the brain that receive pain signals. As a result, the patient experiences less pain since the brain is prevented from receiving pain signals. Anesthesia also works by numbing the area where the procedure occurs, reducing the amount of pain experienced.
Anesthesia is a safe and effective way to reduce pain during medical procedures. It can be administered in various ways and effectively blocks pain signals from the body to the brain. Anesthesia also works by numbing the area where the procedure occurs and slowing down the production of neurotransmitters responsible for sending pain signals.
Types of Anesthesia and Their Effects
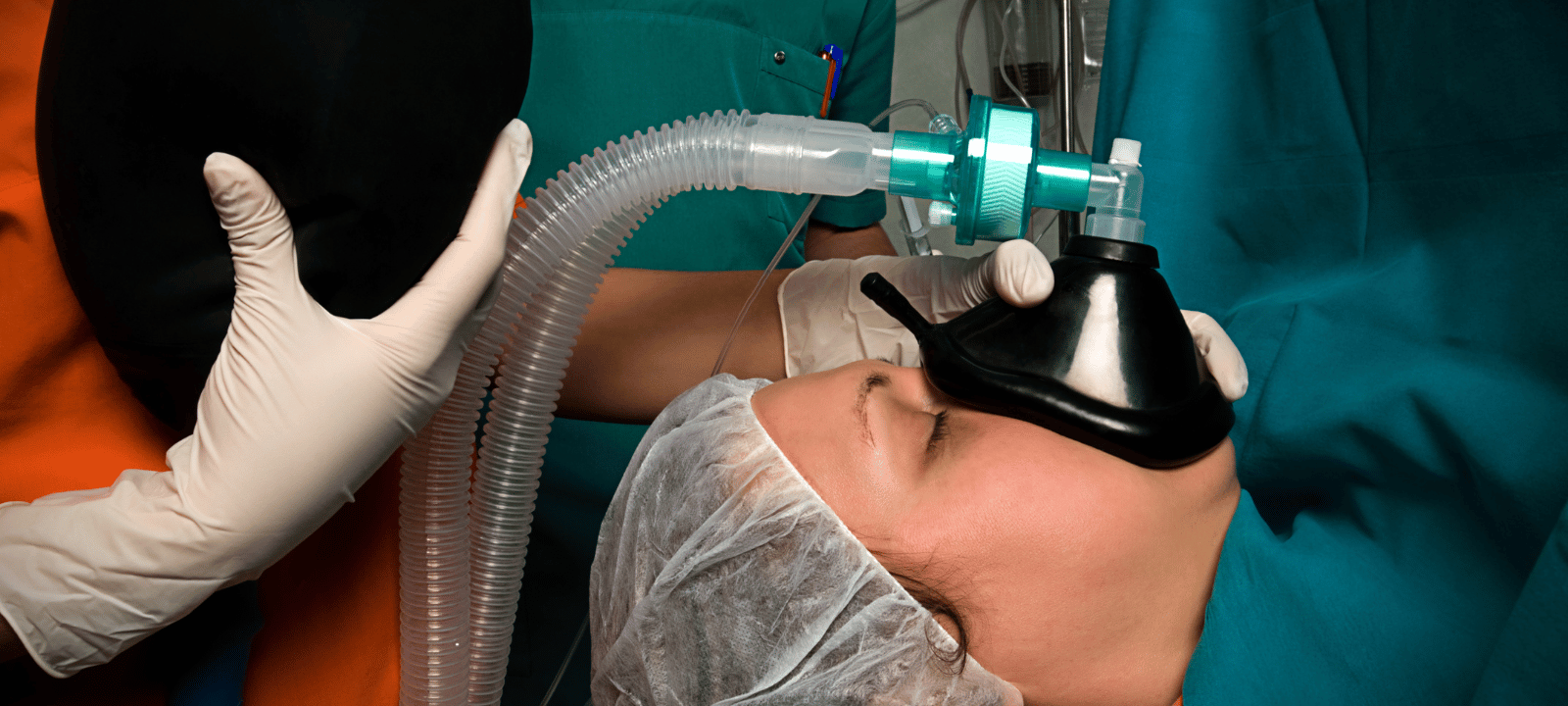
Anesthesia is a type of medication that is used to block pain and other sensations during medical procedures. There are several types of anesthesia, each with its unique effects.
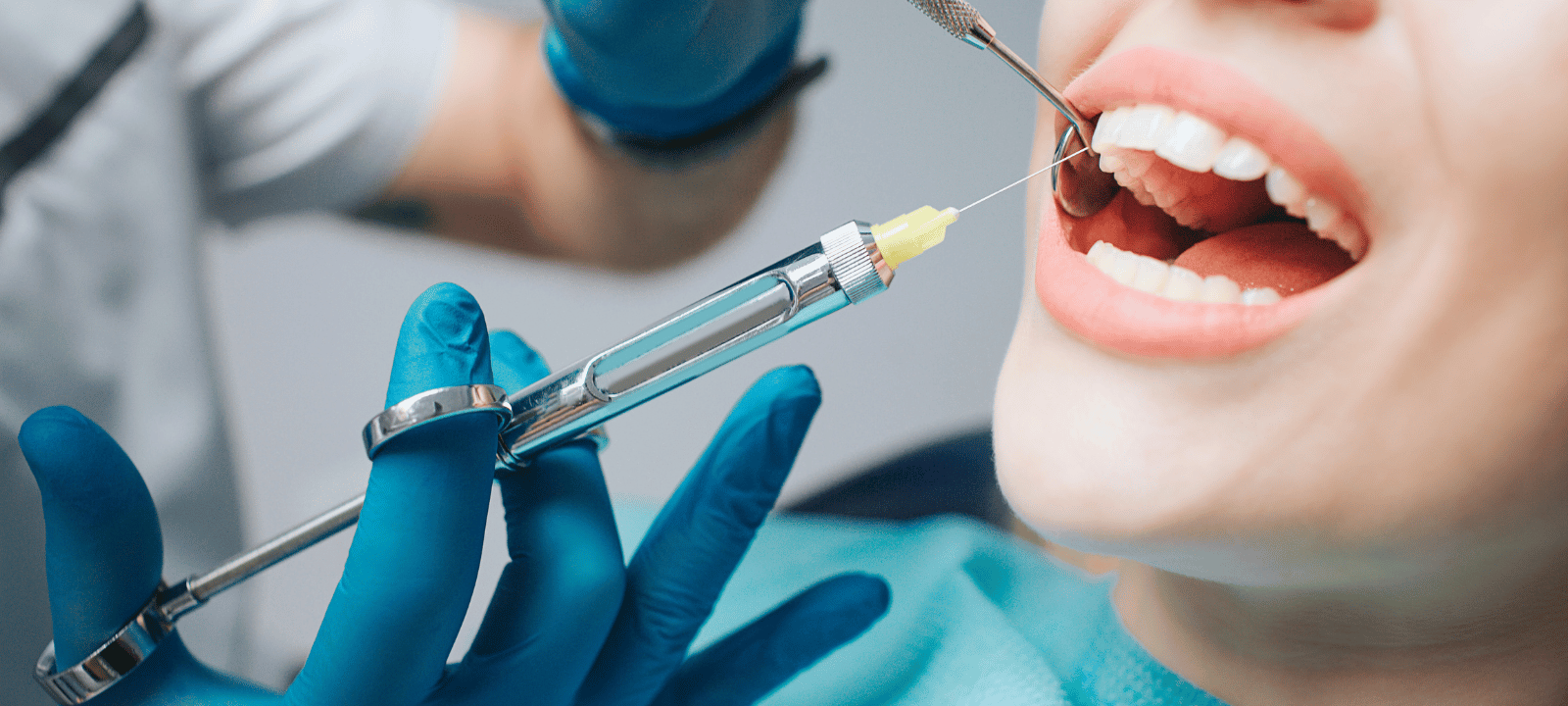
Local Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is the most common type for minor procedures. It numbs the body area where the procedure occurs, but the patient remains conscious. This type of anesthesia is typically used for minor surgeries, such as removing a mole or wart.
Regional anesthetic: Regional anesthetic is employed for trickier treatments like joint replacement surgery. This type of anesthesia numbs an entire body region, such as the arm or leg. The patient remains conscious but may not remember the procedure.
General Anesthesia is used for more severe surgeries like heart bypass. This type of anesthesia puts the patient into a deep sleep. The patient is not conscious and does not remember the procedure.
The effects of each type of anesthesia depend on the type and amount of medication used. Typically used for quick operations, local anesthetic only has mild adverse effects, such as numbness or tingling. Using regional anesthetic during trickier operations might result in more severe side effects, including nausea and vomiting. More significant side effects, such as disorientation or memory loss, might result from general anesthesia, which is used for more complicated procedures.
Each type of anesthesia has its advantages and disadvantages. Local anesthesia is the least invasive type of anesthesia and has the least amount of side effects. Regional anesthesia is more invasive and can cause more severe side effects. General anesthesia is the most invasive and has the most serious side effects.
Overall, anesthesia is a safe and effective way to block pain and other sensations during medical procedures. Each type of anesthesia has its advantages and disadvantages, so discussing your options with your doctor before undergoing any procedure is essential.
Potential Side Effects of Anesthesia

Most people know that anesthesia might make you sleepy, but they might not know of any other adverse effects. Depending on the kind of anesthetic used and the patient’s response, anesthesia may result in various side effects ranging from minor to severe.
Some of the most common side effects of anesthesia include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, and dry mouth. Other potential side effects include shivering, chills, sore throat, headache, and fatigue. More severe side effects, such as heart attack, stroke, and allergic reactions, may sometimes happen.
Some people may be more likely to experience side effects than others. Factors such as age, weight, medical history, and the type of anesthesia used can all affect the likelihood of experiencing side effects.
Fortunately, there are techniques to reduce the possibility of anesthesia-related side effects. For instance, paying attention to instructions given by your doctor or anesthesiologist before the surgery is crucial. This includes avoiding eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure and informing your doctor of any allergies or medical conditions you may have. Additionally, following your doctor’s post-operative instructions is essential, such as taking medications as prescribed and avoiding certain activities.
Overall, anesthesia can cause various side effects, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the potential side effects and how to minimize the risk of experiencing them is essential. By following all instructions provided by your doctor or anesthesiologist, you can help ensure that your experience with anesthesia is as safe and comfortable as possible.
How Anesthesia Makes You Sleep
Anesthesia is a powerful tool medical professionals use to help patients sleep during medical procedures. It works by obstructing the nerve impulses that bring on pain and other feelings. Doing this allows the patient to relax and fall asleep, allowing the medical team to perform their procedure with minimal discomfort or risk.
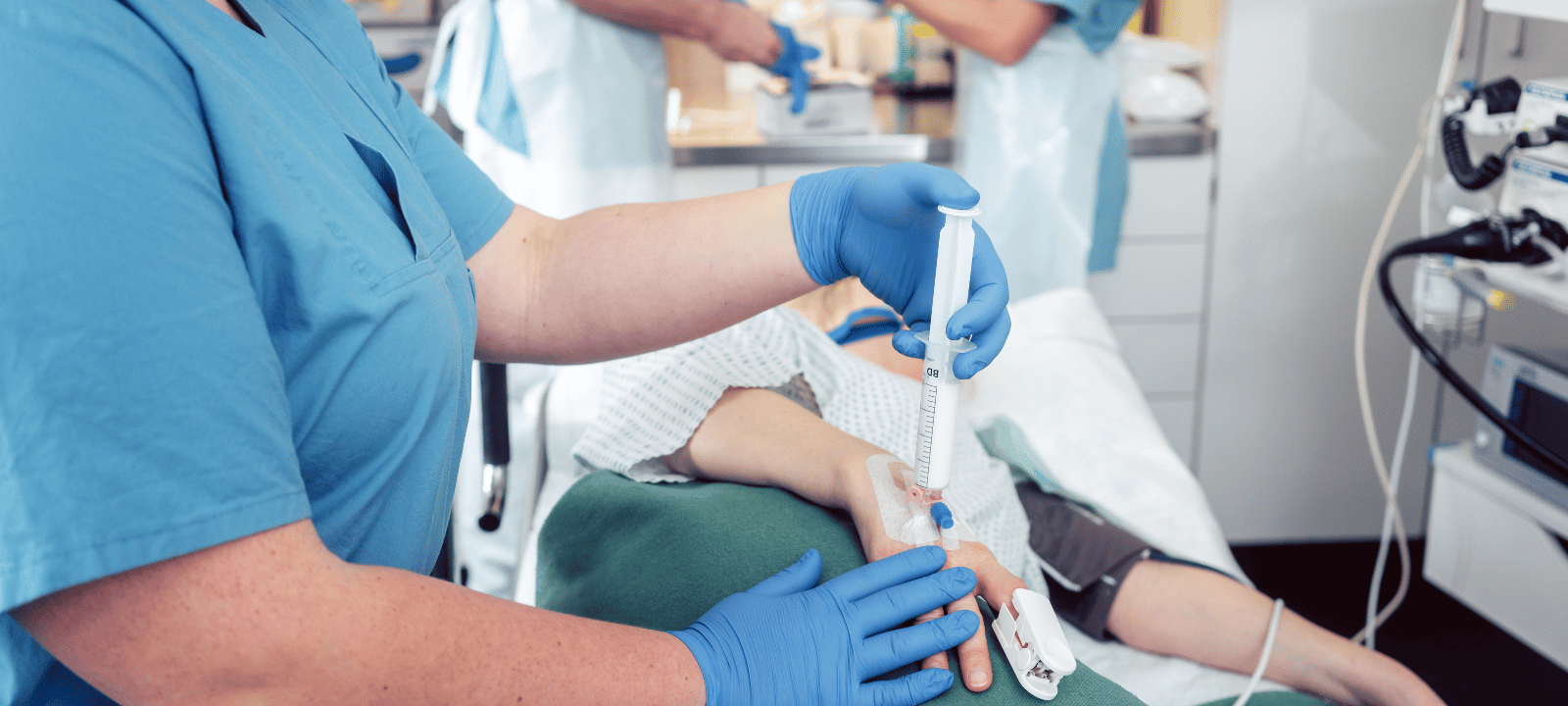
There are several different ways that anesthesia can make you sleep. The most common is through intravenous (IV) drugs, injected directly into the bloodstream. These drugs work quickly to induce sleep, often within minutes. Other types of anesthesia, such as inhalation or topical, can also make you sleep.
In addition to the drugs used to induce sleep, anesthesia also affects the body in other ways. It can slow down the heart rate and breathing rate, as well as decrease blood pressure. This helps the patient to relax and fall asleep more easily. Additionally, it might lessen pain perception, enabling the medical staff to carry out their treatment painlessly.
When undergoing anesthesia, it is essential to be as comfortable as possible. To ensure this, following the medical team’s instructions is crucial, including taking any medications prescribed to help you relax and sleep. It is also essential to get plenty of rest before the procedure, as this can help to reduce any anxiety or stress that may be present. Additionally, it is essential to communicate any concerns or questions you may have to the medical team, as they can provide helpful advice and tips on sleeping more comfortably during anesthesia.
Conclusion
Medical anesthesia as a potent tool to guarantee that patients get the treatment they need without suffering pain or discomfort. It is a safe and efficient approach to guarantee that operations and other medical procedures go off without a hitch. Anesthesia suppresses feeling by obstructing brain messages that go to the body. There are several varieties of anesthetics, and each one has potential drawbacks. Before undertaking any medical treatment, it is essential to go through any possible side effects with a medical specialist.
Anesthesia also has the added benefit of making patients sleep during the procedure. This is especially beneficial for more complex and lengthy procedures, as it allows the patient to rest and recover while the procedure is being performed. Anesthesia is a secure and reliable approach to guarantee that medical operations go off without a hitch.